Cycling – Sustainable Urban Mobility

History of Cycling in Nepal
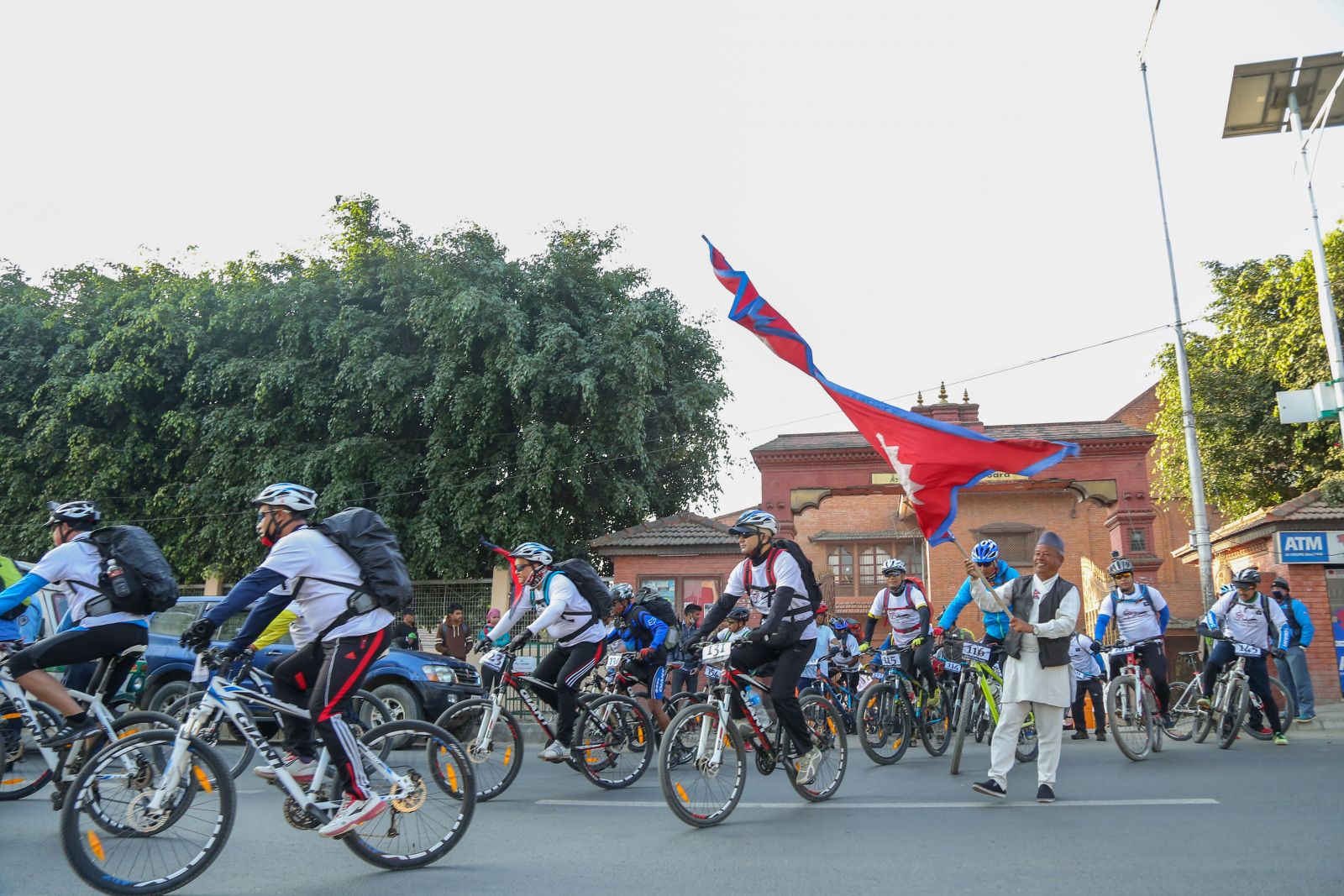
Cycling history in Nepal is shorter compared to western countries. In Nepal, cycling started as a means of transport a little less than a century ago. In the mid-eighties, tourists from the west introduced mountain bikes for recreation and touring activities in Nepal.
Nepal Cycling Association(NCA) encourages district associations and its stakeholders to promote cycling culture among the general public. NCA believes that cycling culture helps tackle burning global issues of climate change, global warming cutting down the production of CO2 emission. It helps to control air pollution and traffic congestion in urban areas. It benefits tourism around the countryside. Cycling helps to enhance health of people and contributes to environment by helping cut down the CO2 emission.

Types of Bicycles
Commuting bicycles are also called “commuter” or “urban” bicycles, although many of the bicycles listed on this page can be used quite well for riding and commuting in a city.
BMX bicycles are popular with kids because of their small size, but they are used by adults and kids alike for various styles of trick and stunt riding.
Mountain bicycles are designed for riding rough off-road trails. They have flat or upright handlebars and a very low gear range for pedalling up steep trails. Most mountain bicycles have some type of shock absorbers or suspension.
Road bicycles are designed to be ridden fast on smooth pavement. They have smooth, skinny tires and “drop” handlebars, and can be used for on-road racing.
Track/Fixed-Gear Bicycles or fixies are designed to be ridden on a velodrome, which is a banked oval track specifically for bicycle racing.
Electric bicycles – more commonly known as e-bikes – provide power assistance to help the rider get to their destination without exerting themselves.
Portal bicycles are human-powered vehicles designed and constructed specifically for transporting loads rather than just commuting.
Parts of a Bicycle
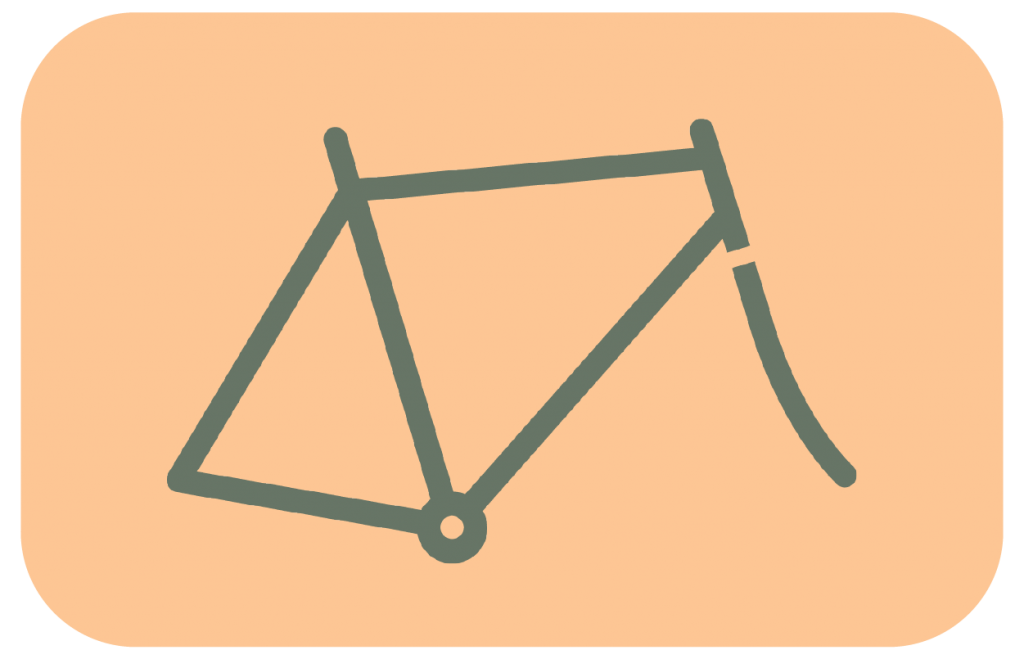
The frame is the most important part of the bicycle. Not only is the frame the one that holds the entire bike up and together.
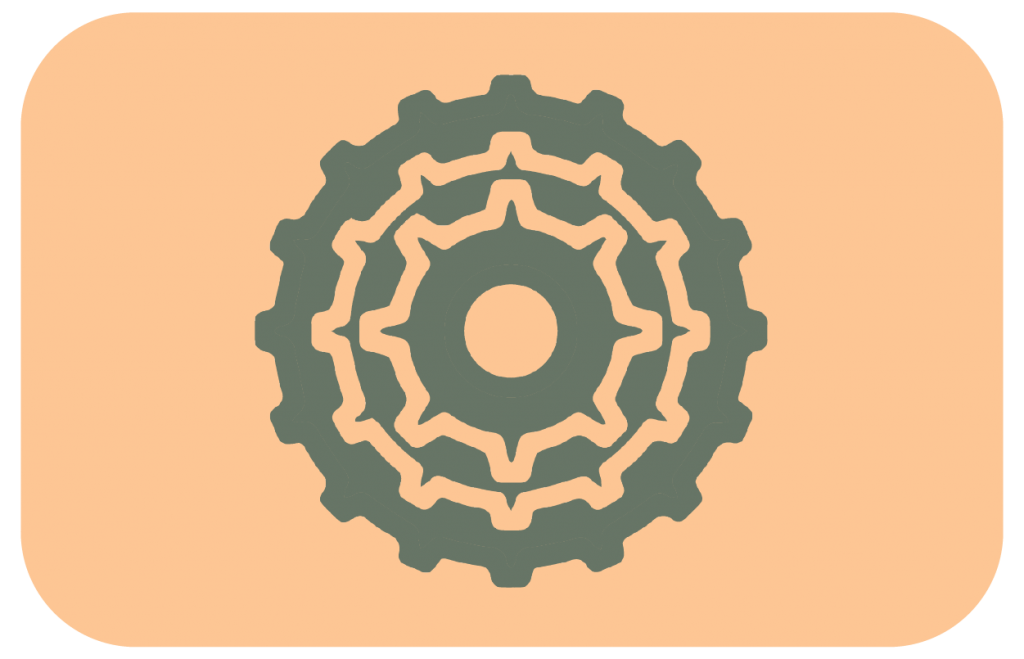
The cassette is the gear mechanism on a geared cycle. It is located at the centre of the rear wheel and consists of a cluster of chromium-molybdenum steel sprockets.
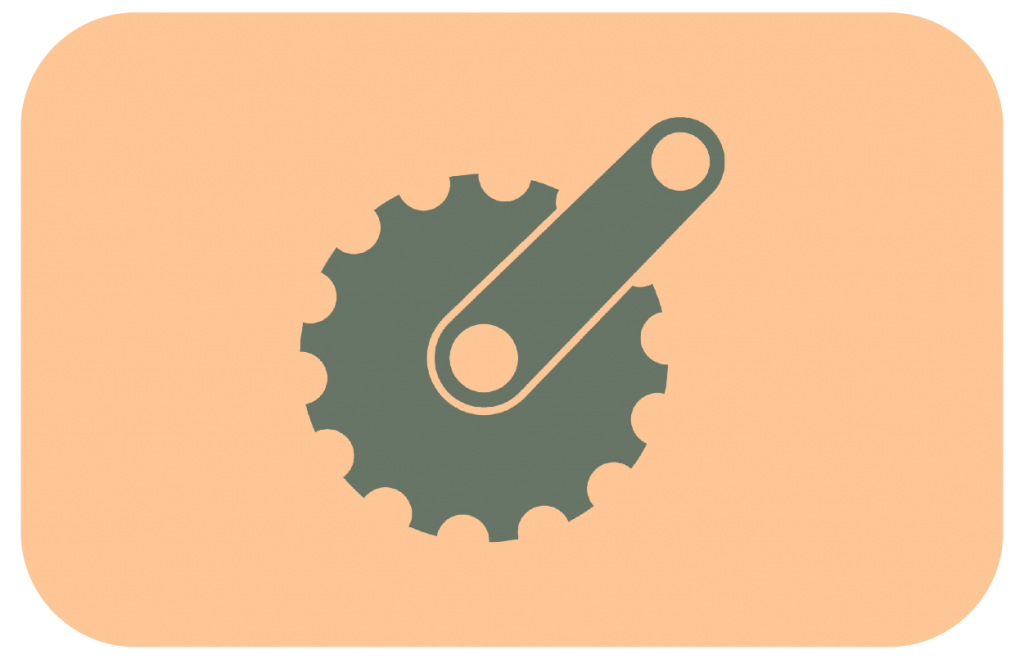

The crankset converts the reciprocating motion of the rider’s legs into rotational motion used to drive the chain or belt, which in turn drives the rear wheel.
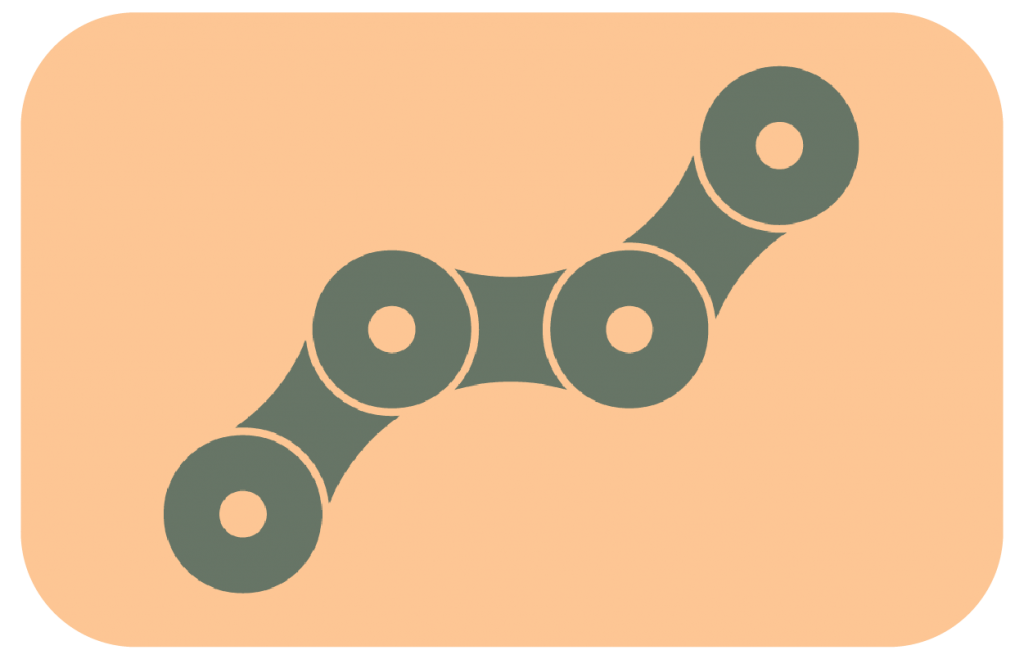
Chain is composed of hundreds of plates, links, and rollers, the chain contains more moving parts than the rest of your bicycle combined.
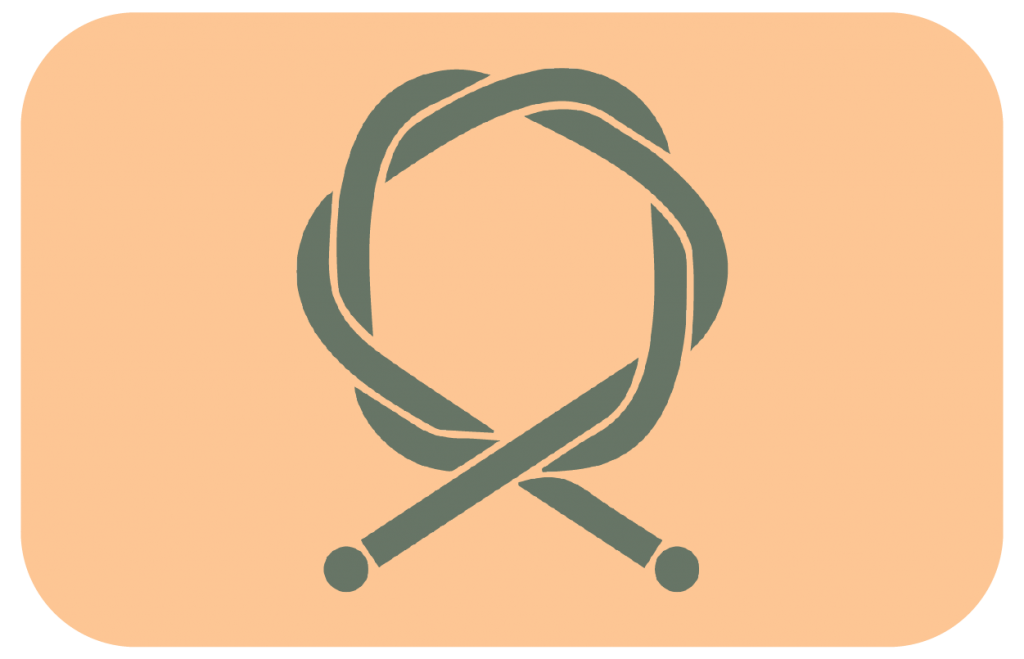
Cables are used in the brake components to change gears or stop your ride. Cables connect each shifter with its derailleur and each brake lever with its caliper.
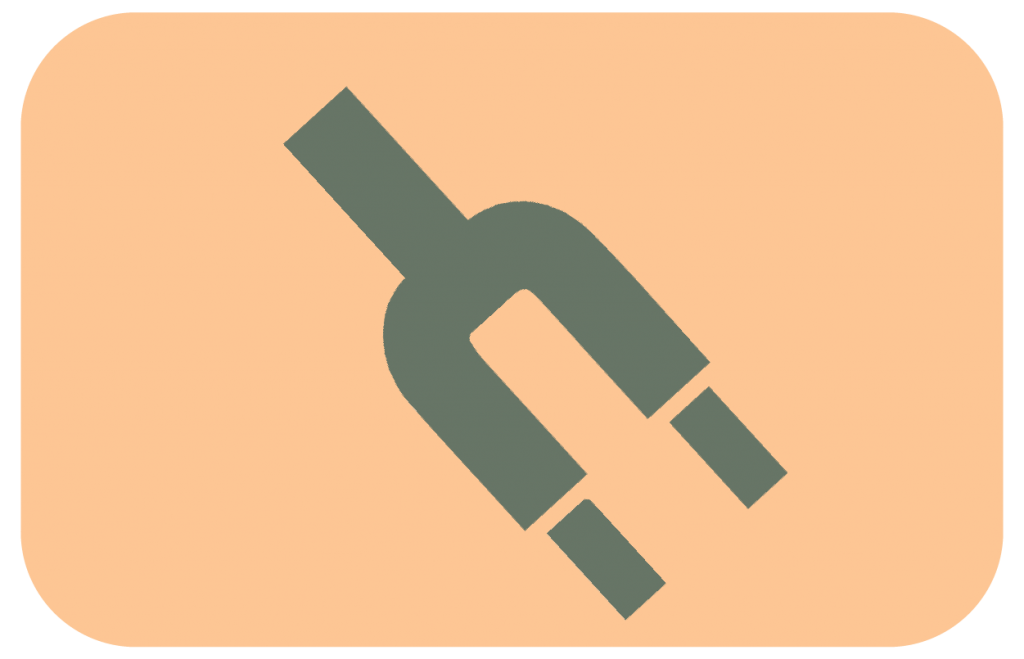
The suspension lets the wheels move up and down to absorb small bumps while keeping the tires in contact with the ground for better control. It also helps the rider and bike absorb large shocks when landing jumps.
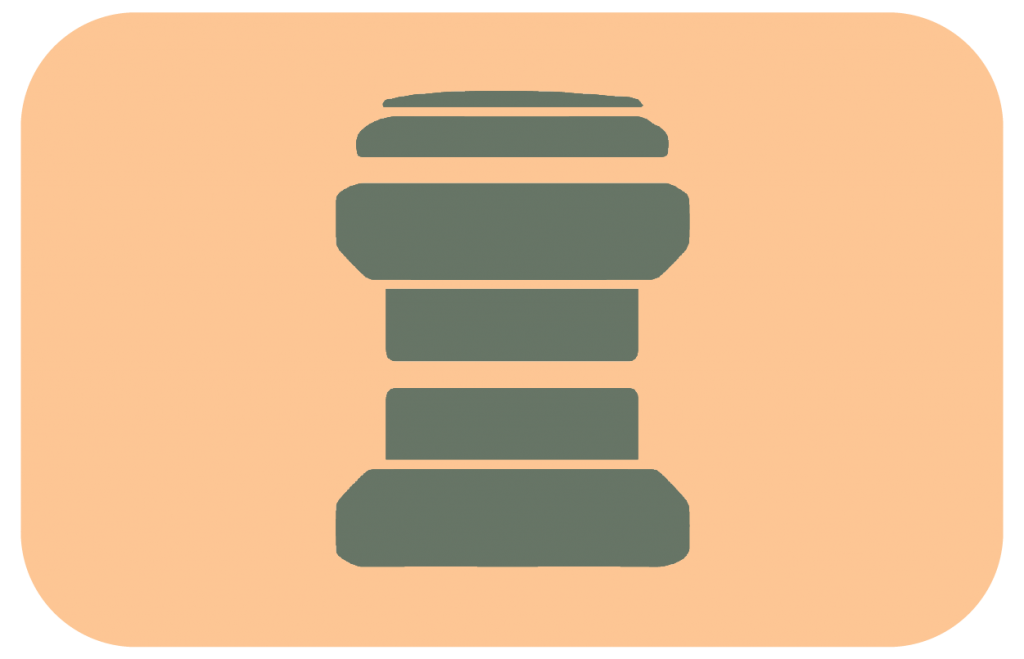
The headset is the interface between the fork to the bike frame, holding it securely in place while allowing it to rotate to steer.
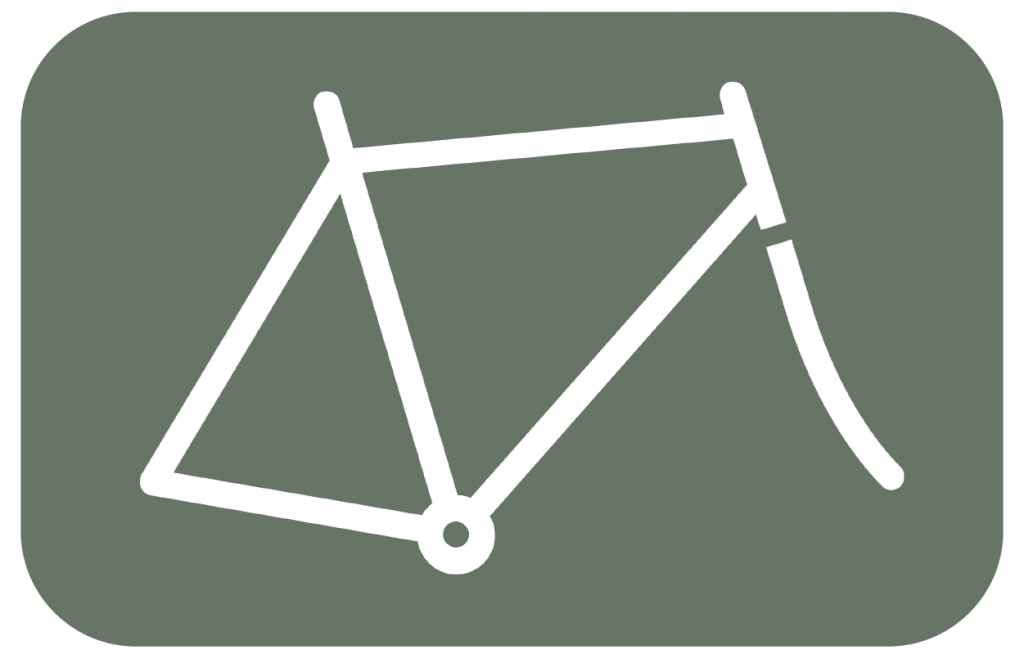
ABC Check
Before you head out on a ride do this really useful “ABC Quick Check ” to ensure a safe ride. Check the sidewall of the tire and inflate tires to the rated pressure using the Gauge as indicated on the sidewall. Have a look at your brakes, check the brakes and cables to make sure they aren’t worn down. Always check that the chain is clean and lubricated. Check your quick-release skewers on your wheels. Make sure they are tight enough to keep your wheels on. Take a quick ride to check if derailleurs and brakes are working properly.
M Check
The M check is another way to make sure your bike is safe to ride. Check the quick release is tightly secured pointing up towards the handlebar stem (or as close as you can get). Check to see if your headset (handlebars and stem) is loose. Check the brakes are fully working
Check the pedals are fixed securely to the crank and spinning freely. Your chain should be clean, oiled and clear of debris. Your saddle should be at the correct height, completely flat and not tilted up or down. Do the same checks as with the front wheel.







